From Agustinas to Zamora, 290 streets can be considered from the infantry city. It forms the main nucleus of the most vivicing path, and it is a dense network in the center to which other methods are added, and it is a transformation in the model that does not reach the neighborhoods. However, it is not an exclusive pedestrian area, who have to share it with cars and already comprehensive cookies. It also did not develop on an equal footing and this type of street is very rare in the most intense neighborhoods.
According to report data, the capital has 44 km from pedestrian streets, and 15 % of all its roads. According to municipal information, there are 290 streets and squares that can be considered infantry and add to this. This makes Salamanca one of the most distorted cities in Spain, the fourth in the distance and the fifth in the percentage.
This frame is the land in which Salamanca has become very functional, because it is one of the easily accessible cities in the main walking services: the majority of the population has schools, health centers and entertainment … within a 15 -minute radius on foot.
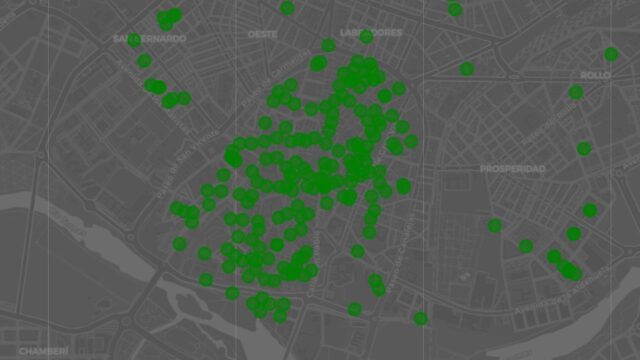
However, as evident from the lower map, the distribution is very unequal, and the pedestrians have made a lot in the center and very few in the neighborhoods, as it depends only on the new presence. If the Salamanca Center is an area where approximately one hundred percent can walk in the outer crown, things differ completely.
Green points of the map indicate all pedestrian paths that spread to the city. It can also be seen, its concentration is very high in the first round of Ronda, the interior of the central almonds, which contains the historical center and 90 % of the region already.
On the other hand, the green points outside that first episode that determines the center. Those that appear corresponding to the work of the internal squares of Pizarral or San Bernardo, the neighborhoods where the pedestrian streets were exposed to the blocks. The same thing happened in the Blanco neighborhood with the improvement of some streets that have benefited from giving more pedestrians.
It also appears in those younger neighborhoods, such as Zurguén, and where the urban plot has changed, as is the case in the streets of prosperity. On the other hand, densely populated neighborhoods such as Garrido, Salesas, El West, Labradores, Tejares, Buenos Aires, or roll completely lacking pedestrian streets or exceptions.
-
Residential streets
The 20th boundary and infantry priority
The infantry street coordination is completed, with a road at the same level as the sidewalks, panel pavement and the lowest parking lots (or nothing) other formats that also gain the force that gives importance and priority to pedestrians, but without getting rid of the blood circulation shot.
This is the state of the above streets of prosperity or the distinctive residential areas in the neighborhoods of San Jose or Roll Commonirus a few years ago. These are large spaces with special signs in which the speed is reduced to 20 km/HY indicates that the possibility of playing or inserting them on the way is referred to. Another shape is the streets where bicycles and cars share the road, the last of which is, on farmers.
-
School streets
Less cars near schools
In addition, the city council is developing access to the streets of schools, which affects 41 street Where the presence of cars will be limited to increasing infantry security.
When the works are finished, the affected streets will become one platform, with wider sidewalks, public lighting, directing and electricity and communications networks. Car parks will be reduced, which leads to the disposal of parking lots on both sides of the streets, leaving an area for the largest sidewalks; To compensate for this, 515 areas of parking will be enabled in Chinkibarra and Respiry. Performing with new urban furniture (42 new banks and 61 banks) is rounded and the new vegetation (200 trees and 1057 bush) is to extend the green infrastructure in the city’s neighborhoods.
The goal is to remove cars from school areas and stop the habit of leaving children “to the door”, which is the practice of circulatory problems and insecurity. But the fact is that these measures are not, at the present time, enough to eliminate the dual class.